| layout | title | nav_order |
|---|---|---|
default |
Inheritance |
16 |
In C++, inheritance is a process in which one object acquires all the properties and behaviors of its parent object automatically. In such way, you can reuse, extend or modify the attributes and behaviors which are defined in other class.
In C++, the class which inherits the members of another class is called derived class and the class whose members are inherited is called base class. The derived class is the specialized class for the base class.
Code reusability: Now you can reuse the members of your parent class. So, there is no need to define the member again. So less code is required in the class.
C++ supports five types of inheritance:
1- Single inheritance
2- Multiple inheritance
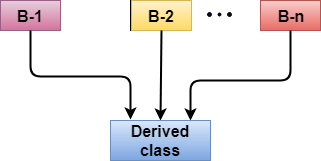
3- Hierarchical inheritance
4- Multilevel inheritance
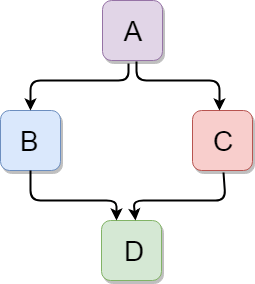
5- Hybrid inheritance
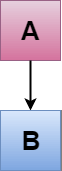
Single inheritance is defined as the inheritance in which a derived class is inherited from the only one base class.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Account {
public:
float salary = 60000;
};
class Programmer: public Account {
public:
float bonus = 5000;
};
int main(void) {
Programmer p1;
cout<<"Salary: "<<p1.salary<<endl;
cout<<"Bonus: "<<p1.bonus<<endl;
return 0;
} Output
Salary: 60000
Bonus: 5000
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Animal {
public:
void eat() {
cout<<"Eating..."<<endl;
}
};
class Dog: public Animal
{
public:
void bark(){
cout<<"Barking...";
}
};
int main(void) {
Dog d1;
d1.eat();
d1.bark();
return 0;
} Output
Eating...
Barking...
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Animal {
public:
void eat() {
cout<<"Eating..."<<endl;
}
};
class Dog: public Animal
{
public:
void bark(){
cout<<"Barking..."<<endl;
}
};
class BabyDog: public Dog
{
public:
void weep() {
cout<<"Weeping...";
}
};
int main(void) {
BabyDog d1;
d1.eat();
d1.bark();
d1.weep();
return 0;
} Output
Eating...
Barking...
Weeping...
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class A
{
protected:
int a;
public:
void get_a(int n)
{
a = n;
}
};
class B
{
protected:
int b;
public:
void get_b(int n)
{
b = n;
}
};
class C : public A,public B
{
public:
void display()
{
std::cout << "The value of a is : " <<a<< std::endl;
std::cout << "The value of b is : " <<b<< std::endl;
cout<<"Addition of a and b is : "<<a+b;
}
};
int main()
{
C c;
c.get_a(10);
c.get_b(20);
c.display();
return 0;
} Output
The value of a is : 10
The value of b is : 20
Addition of a and b is : 30
Ambiguity can be occurred in using the multiple inheritance when a function with the same name occurs in more than one base class.
Let's understand this through an example:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class A
{
public:
void display()
{
std::cout << "Class A" << std::endl;
}
};
class B
{
public:
void display()
{
std::cout << "Class B" << std::endl;
}
};
class C : public A, public B
{
void view()
{
display();
}
};
int main()
{
C c;
c.display();
return 0;
} Output
error: reference to 'display' is ambiguous
display();
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class A
{
protected:
int a;
public:
void get_a()
{
std::cout << "Enter the value of 'a' : " << std::endl;
cin>>a;
}
};
class B : public A
{
protected:
int b;
public:
void get_b()
{
std::cout << "Enter the value of 'b' : " << std::endl;
cin>>b;
}
};
class C
{
protected:
int c;
public:
void get_c()
{
std::cout << "Enter the value of c is : " << std::endl;
cin>>c;
}
};
class D : public B, public C
{
protected:
int d;
public:
void mul()
{
get_a();
get_b();
get_c();
std::cout << "Multiplication of a,b,c is : " <<a*b*c<< std::endl;
}
};
int main()
{
D d;
d.mul();
return 0;
} Output
Enter the value of 'a' :
10
Enter the value of 'b' :
20
Enter the value of c is :
30
Multiplication of a,b,c is : 6000